High-level Overview of NR Release 15
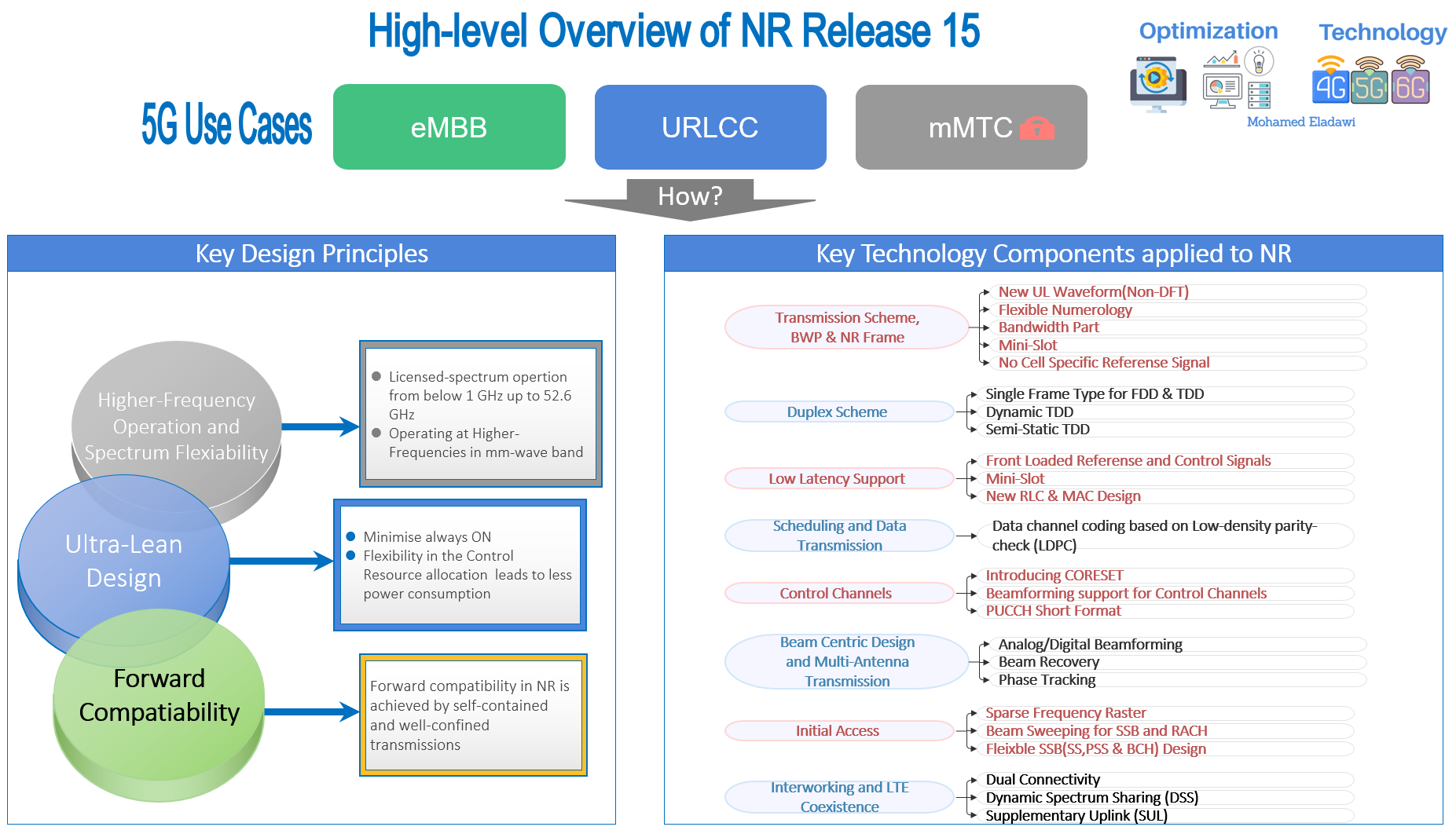
- The technical work of NR was initiated in 2016 as a study item in 3GPP release 14. The first specification of NR Release 15 was limited to non-standalone NR operation. See the below 3GPP timeline for 5G evolution to fulfill the 5G vision
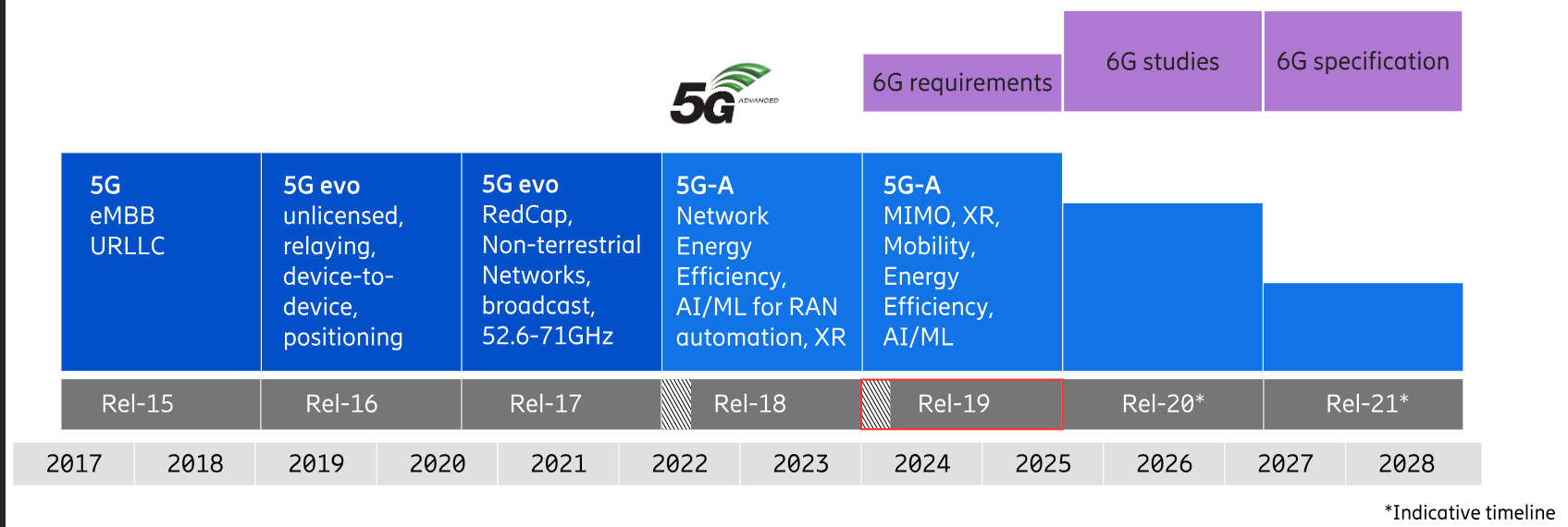
- 5G wireless access is being developed with three broad use case families in mind:
- Enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB)
- Massive machine-type communications (mMTC)
- Ultra-reliable low-latency communications (URLLC)
- NR Release 15 is the first version of NR. During the development, the focus was primarily on eMBB and URLCC Services to some extent.

The 5G use cases and the other benefits offered compared to LTE are primarily related are the dependable on the following 3 key design principles:
- Higher-Frequency Operation and Spectrum Flexibility in which:
- It supports Licensed-spectrum operation from below 1 GHz up to 52.6 GHz.
- Operation at Higher-Frequencies in the mm-wave band offers the possibility for large amounts of spectrum and associated very wide transmission bandwidths .
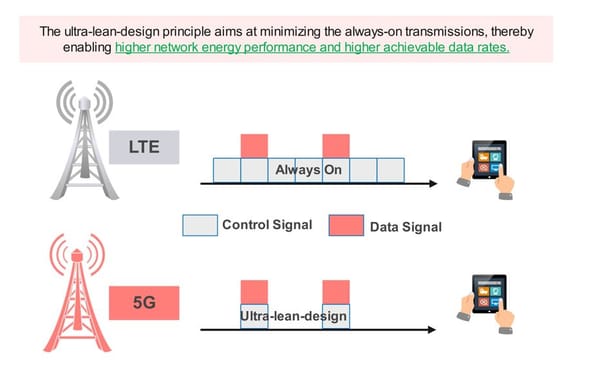
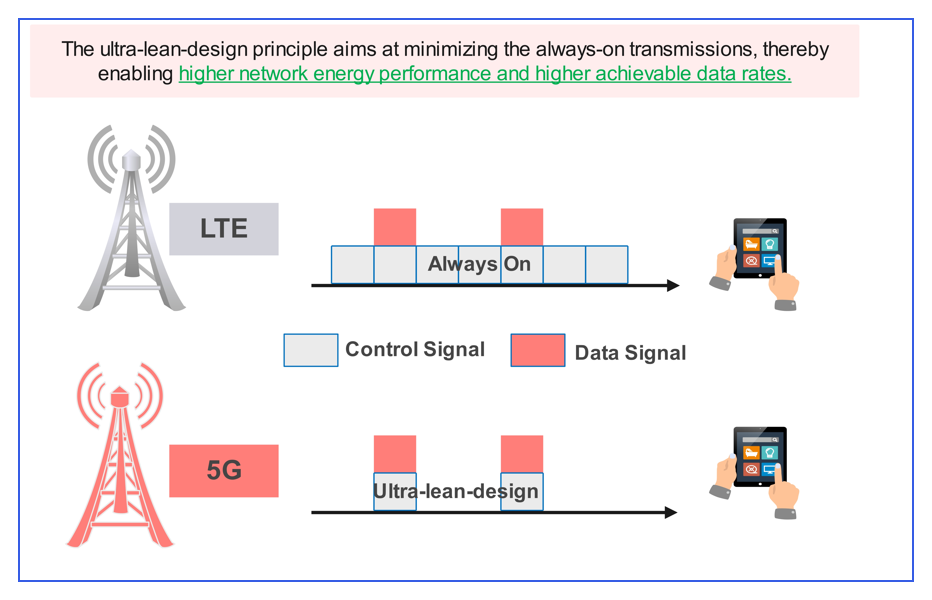
- Ultra-Lean Design where:
- It aims to Minimize always-on transmission, , thereby enabling higher network energy performance and reduces network operational expenses and enables higher achievable data rates.
- It offers flexibility in the Control Resource allocation leads to less power consumption.
- Forward Compatibility, where 3GPP agreed on some basic design principles summarized as below:
- Maximizing the amount of time and frequency resources that can be flexibly utilized or that can be left (Example reserved resources which can be used for LTE-NR Co-existence)
- Minimizing the transmission of always on-signals ( as explained in the Ultra-lean design).
- Confining signals and channels for physical layer functionalities within a configurable/allocable time/frequency resource.
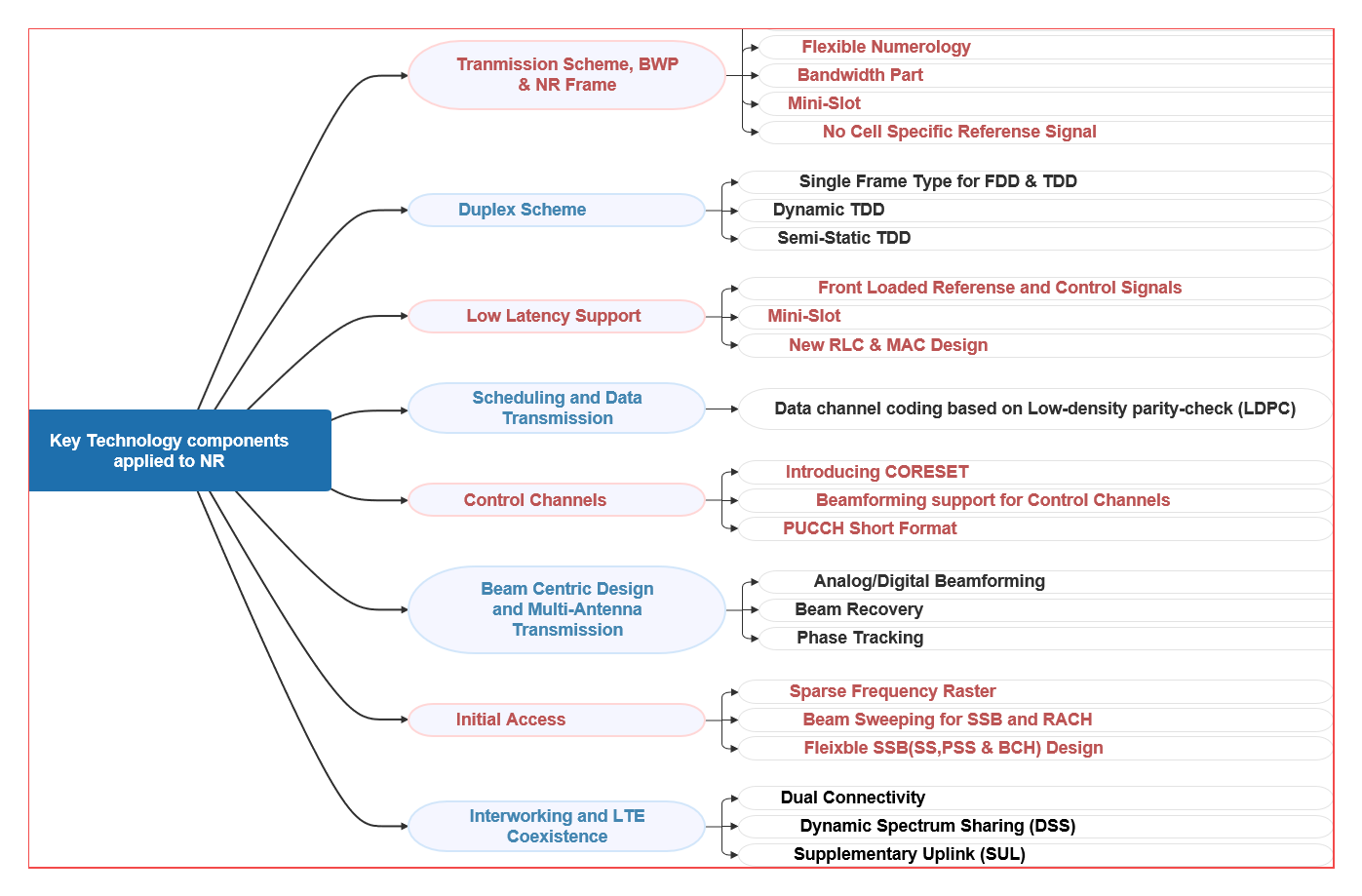
What are the fundamental technology pillars and components utilized in NR to realize the specified Use Cases and design principles?
- The following picture summarize the key technology components applied to NR:
- Transmission Scheme, BWP & NR Frame. i.e. Flexible Numerology
- Duplex Scheme. i.e. Dynamic TDD
- Low Latency support. i.e. Front Loaded DMRS
- Scheduling and Data Transmission. i.e. LDPC
- Control Channels. i.e. CORESET
- Beam Centric Design and Multi-Antenna Transmission. i.e. Beam Recovery
- Initial Access. i.e. Beam sweeping for SSB and RACH
- Interworking and LTE. i.e. Dynamic Spectrum Sharing
Good References & Study Sources:
https://www.qualcomm.com/content/dam/qcomm-martech/dm-assets/documents/5G-NR-Release-15.pdf
5G NR: The Next Generation Wireless Access Technology- Page 57 to 70