What is 5G SSB? Meaning and Main Functionality
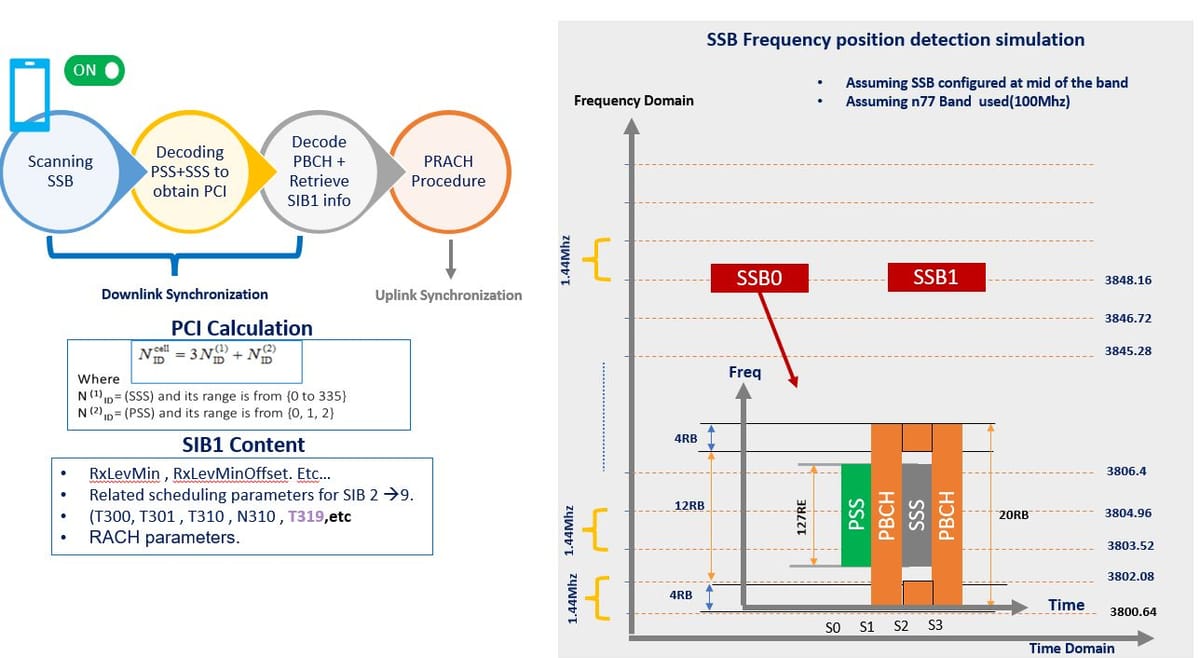
What is SSB?
5G Synchronization Signal Block (SSB) plays a crucial role in cell search and mobility. It consists of:
- PSS (Primary Synchronization Signal)
- SSS (Secondary Synchronization Signal)
- PBCH (Physical Broadcast Channel)
SSB occupies 20 Resource Blocks (RBs) and 4 Symbols in the frequency domain.
How Does UE Detect SSB and Achieve Synchronization?
The User Equipment (UE) follows these main steps to detect the SSB and complete downlink (DL) and uplink (UL) synchronization during the cell search process:
- UE will scan the band to find the SSB frequency location once the UE Power is turned on.
- UE blindly scans the band until detecting SSB Frequency location; UE starts frequency scanning from the bottom of the band.
- After the UE Detected SSB Location, it will start decoding "PSS" Primary synchronization signal, then "SSS" Secondary synchronization signals in sequence to acquire and obtain the "PCI" Primary Cell ID.
- Then the UE will decode "PBCH" Physical broadcast channel to obtain and retrieve "MIB" Master information block and "SIB1" System information block type 1 information which is needed to complete the initial access
- SIB includes all related parameters about RACH
- Lastly, after the Downlink Synchronization has been completed, the UE will start PRACH “Physical random access channel procedure” to complete the uplink Synchronization.
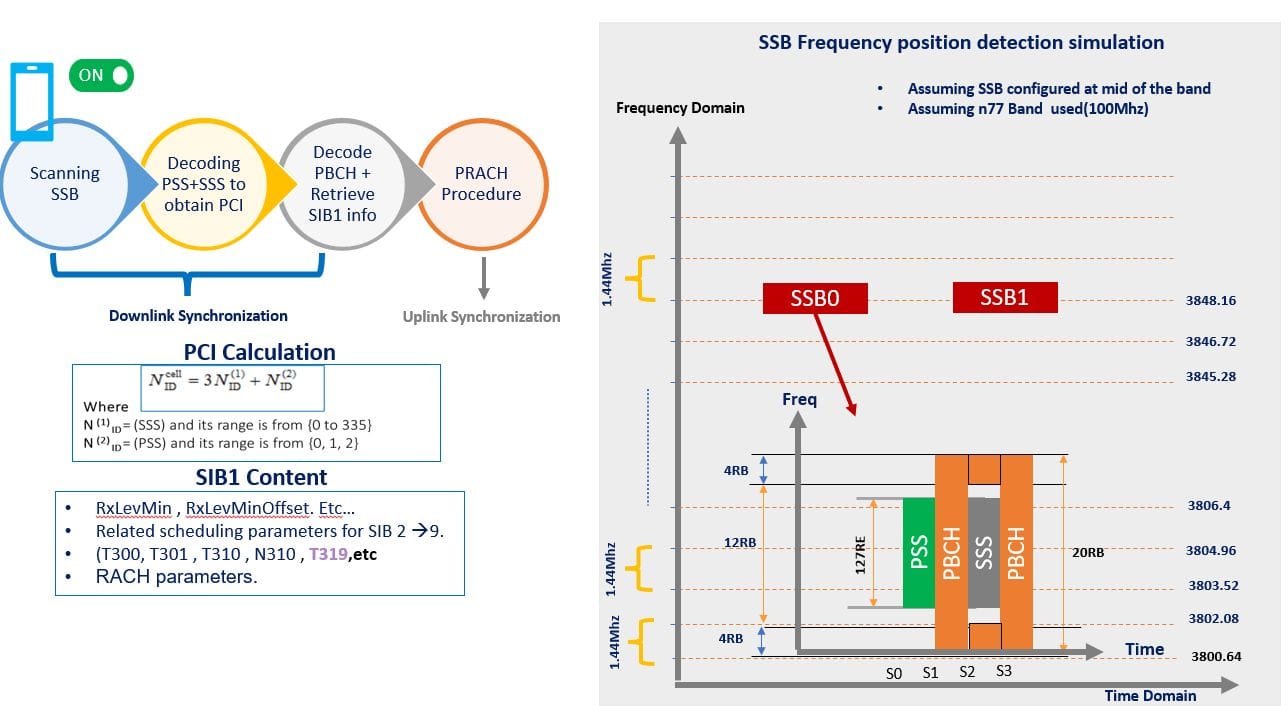
refer to the below video for more details:
Source:
- 5G NR in Bullets.