What is Globally Unique Temporary identifier (GUTI) ❓
- The 4G/5G Globally Unique Temporary Identifier (GUTI) is a temporary identity used by the network to enhance privacy. The MME assigns it in 4G or AMF in 5G, and the allocated GUTI can be changed at any time by MME/AMF.
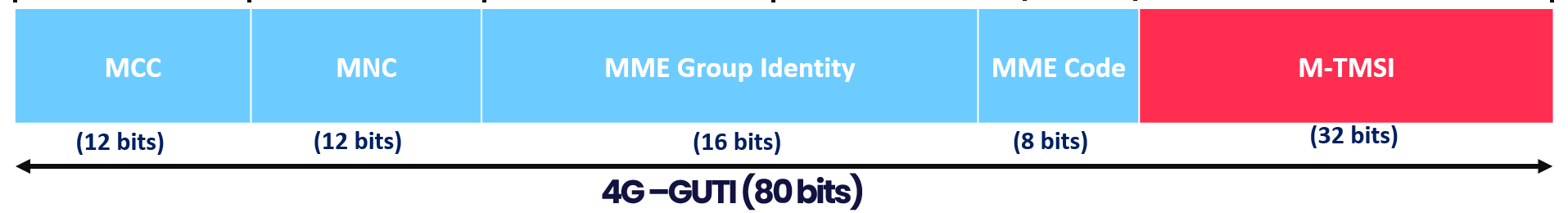
- 4G GUTI has three components. Where:
- PLMN identity - uniquely identifies the network globally (MCC + MNC)
- MME Identity (MMEI) - uniquely identifies the MME within the PLMN
- MME-TMSI (M-TMSI) - uniquely identifies the UE within the MME
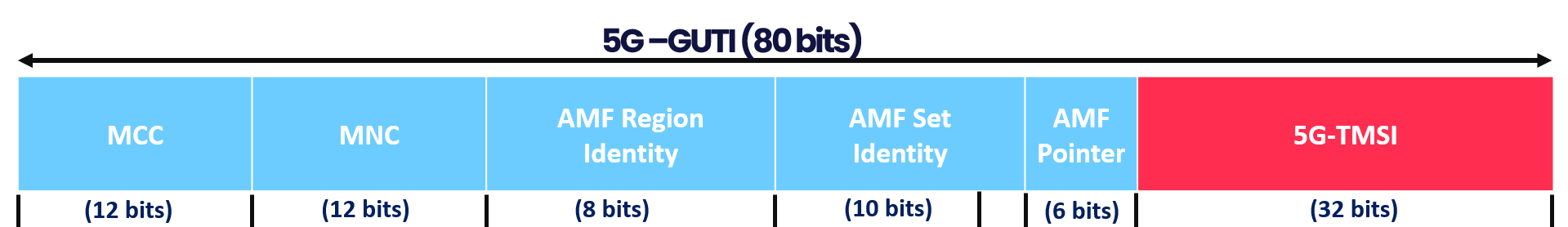
- 5G-GUTI is a concatenation of the (GUAMI) and 5G-TMSI. Where:
- The Globally Unique AMF Identifier (GUAMI) is a concatenation of the PLMN Identity and the AMF Identifier.
- The 5G-TMSI identifies the UE within that AMF
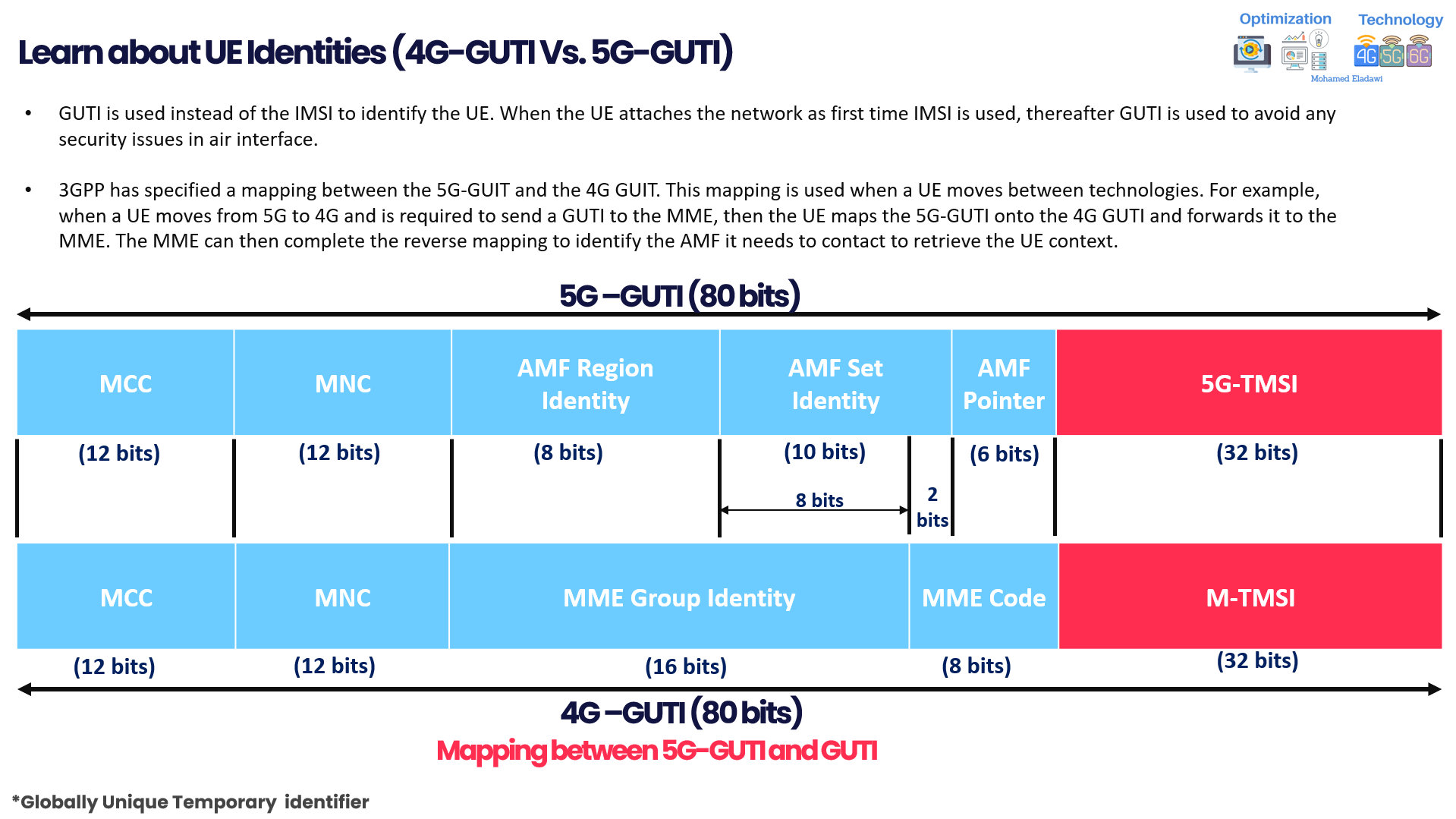
- GUTI takes the place of the IMSI in identifying the UE. When the UE attaches to the network for the first time, IMSI is used. Afterward, GUTI steps in to prevent any security issues in the air interface.
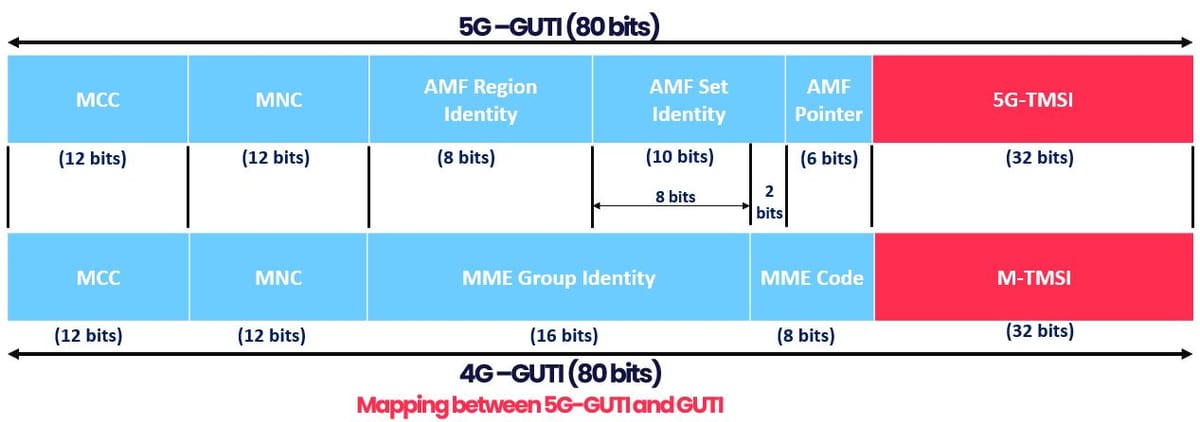
- To facilitate seamless movement between 4G and 5G technologies, 3GPP has specified a mapping between the 5G-GUIT and the 4G GUTI. For example, when a UE transitions from 5G to 4G and needs to transmit a GUTI to the MME; it cleverly converts the 5G-GUTI into the 4G GUTI before forwarding it to the MME.
- The MME then performs a reverse mapping, identifying the specific AMF it needs to contact for retrieving the UE context.
Refer to the below video for more details:
Source:
- LTE in Bullets page 574
- NR in Bullets Page 579